Bureau of Statistics: In 2020, China invested a total of 2,439.31 billion yuan in research and experimental development, a year-on-year increase of 10.2%.
Cctv newsAccording to the website of the National Bureau of Statistics, in 2020, China’s R&D investment continued to grow rapidly, and the investment intensity continued to increase. However, due to the COVID-19 epidemic and other factors, the investment growth rate slowed down, and the national financial expenditure on science and technology decreased compared with the previous year.
I. Research and Experimental Development (R&D) Funds
In 2020, China invested a total of 2,439.31 billion yuan in research and experimental development (R&D), an increase of 224.95 billion yuan or 10.2% over the previous year, and the growth rate dropped by 2.3 percentage points over the previous year. The investment intensity of research and experimental development (R&D) (the ratio to GDP [2]) was 2.40%, 0.16 percentage points higher than the previous year [3]. According to the full-time workload of R&D personnel, the per capita expenditure is 466,000 yuan, an increase of 5,000 yuan over the previous year.
According to the types of activities, the national basic research fund was 146.70 billion yuan, an increase of 9.8% over the previous year; The applied research expenditure was 275.72 billion yuan, an increase of 10.4%; The experimental development expenditure was 2,016.89 billion yuan, an increase of 10.2%. The proportion of funds for basic research, applied research and experimental development is 6.0%, 11.3% and 82.7% respectively.
According to the main body of activities, the R&D expenditure of various enterprises was 1,867.38 billion yuan, an increase of 10.4% over the previous year. Expenditure of government-owned research institutions was 340.88 billion yuan, up by 10.6%; Expenditure of institutions of higher learning was 188.25 billion yuan, an increase of 4.8%. The proportion of expenditure of enterprises, government-owned research institutions and universities is 76.6%, 14.0% and 7.7% respectively.
In terms of industrial sectors, the R&D expenditure of high-tech manufacturing industry was 464.91 billion yuan, and the investment intensity (ratio to operating income) was 2.67%, up by 0.26 percentage points over the previous year. The R&D expenditure of equipment manufacturing industry was 913.03 billion yuan, and the input intensity was 2.22%, up by 0.15 percentage points over the previous year. Among the industrial enterprises above designated size, there are 10 industries whose R&D expenditure exceeds 50 billion yuan, and the funds of these 10 industries account for 73.6% of the R&D expenditure of all industrial enterprises above designated size (see Annex 1 for details).
By region, there are eight provinces (cities) that have invested more than 100 billion yuan in R&D, namely Guangdong (347.99 billion yuan), Jiangsu (300.59 billion yuan), Beijing (232.66 billion yuan), Zhejiang (185.99 billion yuan) and Shandong (168.19 billion yuan). There are seven provinces (cities) whose R&D expenditure intensity (the ratio to regional GDP [4]) exceeds the national average, namely Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Shaanxi (see attached table 2 for details).
II. Financial expenditure on science and technology
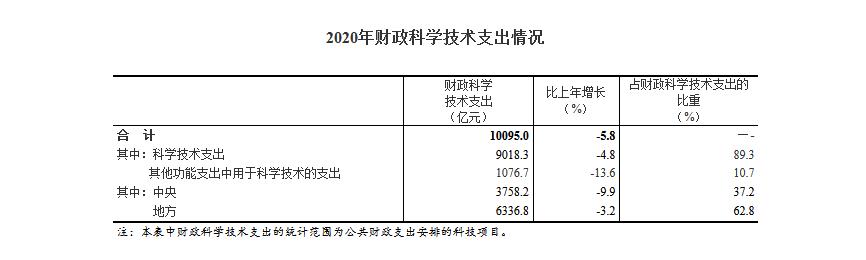
In 2020, the national financial expenditure on science and technology was 1,009.50 billion yuan, a decrease of 62.24 billion yuan or 5.8% over the previous year. Among them, the central fiscal expenditure on science and technology was 375.82 billion yuan, down 9.9%, accounting for 37.2% of the fiscal expenditure on science and technology; The local fiscal expenditure on science and technology was 633.68 billion yuan, down by 3.2%, accounting for 62.8%.